Your application will only run smoothly if the right motor is used. It is therefore important to know exactly what to take into consideration for the selection of a stepper motor – because knowing the key parameters will not only make your purchasing decision easier, it will also guarantee reliable motor performance with minimum wear.
To make your search for the right stepper motor easier, the FAULHABER experts have listed their five most important tips for you in this stepper motor selection guide.
Below you will find out:
2. Why you should always take into account the maximum motor power when selecting a stepper motor.
4. How to determine and deal with the resonance frequency of a stepper motor.
For stepper motor selection, in addition to the size of the required model you also need to know how much power the motor can and should provide in the specific application case. For this reason, it is advisable to first draw up an as precise overview of the application conditions as possible and to compare this with the parameters of the available motors.
Furthermore, we will show you with the help of an example case how you can use the individual parameters to check the suitability of specific stepper motors for the planned application.
The first step is to find out which speed profile the stepper motor must have in order to perform the angular movement required in its specific application area within the specified time frame. When selecting a stepper motor, this means specifically that you should first check whether the speed profile of the selected model fulfills the requirements.
To do so, you determine the load parameters at the motor shaft in two steps:
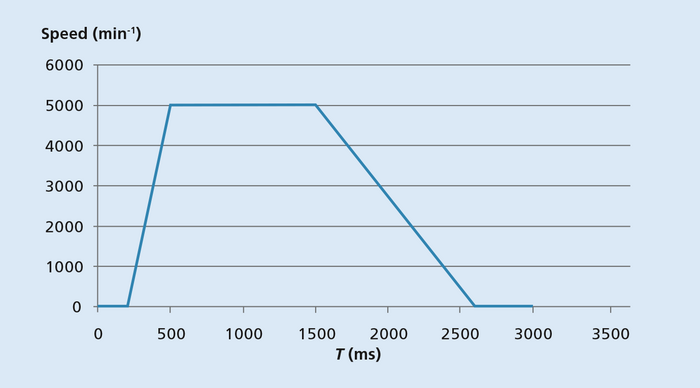
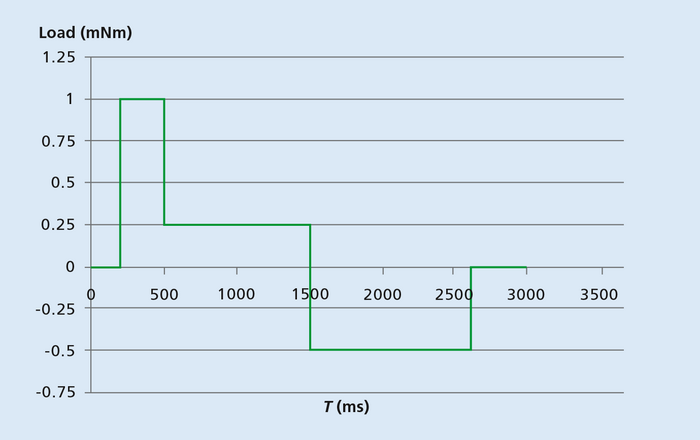
Figure 1 shows two example calculations for the selection of a stepper motor on the basis of the speed profile. Here, a motor with an external diameter of max. 15 mm is required for the planned application. As the dimensions of the stepper motor AM1524 meet these specifications, using the data for this model both, the inertia and the torque, were calculated in order to check whether the speed profile is suitable for the application area.

You can usually find the load parameters of a stepper motor in the torque-speed curves published in the data sheet. As you need these load parameters to compare the requirements of the planned application with the performance and potential limits of the various stepper motors, you should always obtain the manufacturer information for your preferred models before you begin selecting a stepper motor.
To ensure that the selected model delivers the required power, when selecting a stepper motor it is best to base your decision on the operating point at which the application demands the highest values for torque and speed. Here, always select a stepper motor that can deliver the required power without problems and, if necessary, is also able to achieve even higher speeds: In this way you guarantee that the motor will operate properly even under extremely high, unforeseen loads.
Figure 2 shows an application case where the point with the highest ratio between torque and speed is at the end of the acceleration phase. The maximum speed is n = 5,000 rpm and the torque is M = 1 mNm. If, during stepper motor selection, you are unsure whether the selected model is powerful enough, you can base your decision on these parameters by plotting on the torque-speed curve of the motor the point at which the maximum load occurs. In this example, the maximum was determined using the curves for a stepper motor of the AM 1524 series – with the result that the motor will properly satisfy the specified application conditions.
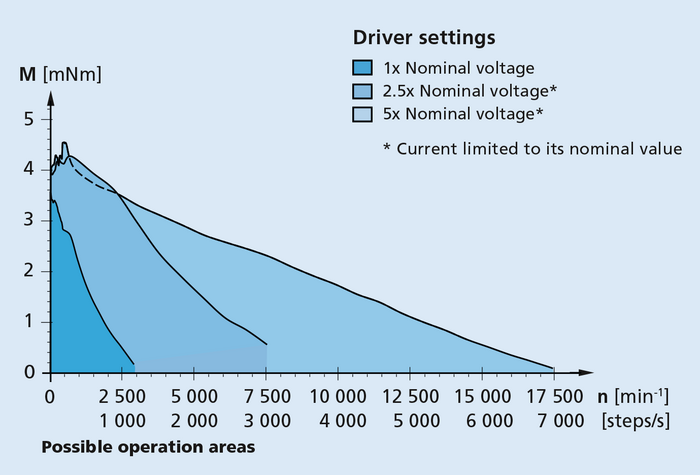
If none of the available models precisely meets the needs of the planned application, you can choose a nearly ideal model when selecting a stepper motor: With the help of a reduction gearhead, you can adapt the load parameters more precisely to the planned application.

If the angular resolution is too low, this does not rule out an otherwise well suited motor: Operation in half-stepping or micro-stepping mode can further increase the angular resolution. However, micro-stepping operation also reduces the accuracy of the motor because the angular error remains constant irrespective of the number of steps.
For this reason, it is advisable to find out how precisely you can adapt the angular resolution to the application conditions before selecting a stepper motor. To do so, determine the optimum angular resolution for the planned application of the stepper motor and compare the optimum with the actual angular resolution of the motor in full-stepping, half-stepping and micro-stepping operation. If none of these three options corresponds to the optimum for the operation of your stepper motor, you can adapt the motor resolution to the requirements of the application by using a gearhead or – if linear movement is required – a lead screw.
The example of stepper motor selection shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 assumes that an angular resolution of 9° is required for the planned application. This means that the selected motor – a FAULHABER stepper motor of the AM1524 series with a full step angle of 15° – is not suitable for full-stepping operation in this case. To achieve a finer resolution, the motor can, however, be operated in half-stepping mode or micro-stepping mode or be combined with a gearhead.
When should I use an encoder with a stepper motor? And can I combine a stepper motor with a lead screw or a gear box?
Our expert Julien Berger will answer your questions and give you an overview about the combination possibilities of FAULHABER stepper motors with different components in order to create the perfect drive system for your application.
Like all oscillating systems, a stepper motor also has a so-called resonance frequency. This is typically in the lower speed range – usually at less than 100 Hz. If the motor is operated at this frequency, disturbances in speed and direction of rotation often occur. As a result, in its resonance frequency range the stepper motor not only runs irregularly, but at worst loses its torque and stops.
To avoid both torque loss and step losses effectively, it is therefore important when selecting the stepper motor to make sure that the oscillations generated by the planned application are not so great that they cause the selected motor to reach its resonance frequency. To this end, determine the optimum speed for the desired application and compare it with the resonance frequency specified in the product data sheet of the respective model.
If it emerges in stepper motor selection that the resonance frequency of this model happens to be in exactly the speed range that would be required for the application, this does not necessary mean exclusion of this drive. Instead of operating the motor in full-stepping mode, with a stepper motor you also have the option of changing to micro-stepping mode – and the higher the number of steps, the better: Dividing the movement into micro-steps can largely offset resonance effects.

Although intensive preparation is indispensable when selecting a stepper motor, ultimately even the most thorough calculation is no substitute for the practical test. Therefore, as soon as you begin making preparations for the purchasing decision, document all parameters as well as all additional factors – e.g. the expected service life of the drive, the price or components such as encoders that the stepper motor can be combined with – on which you will base your selection. This way, you can more easily identify potential discrepancies between the motor and the requirements of the application and, where necessary, alter decisions more efficiently.
You are in the process of selecting a stepper motor and need a data sheet that you can't find anywhere on our website? Or have you already calculated all parameters, but are still unsure which of our motors would be the right one for your planned application? No problem: The experts from FAULHABER will gladly advise you in all matters regarding the selection of your stepper motor.